Normally if you wanted to store data in a Docker container it would be stored in the writable layer of the Docker Container, but this is not an efficient way to store data. So we make use of different Docker storage types. These storage types have a lot of advantages over the default storage method. Persistent data, Transfer data easily and Increase container performance.
Previous Tutorial – How to create Docker File and its Best Practices
Docker Volume Storage
Docker Volumes are basically persistent storage locations for the containers. They are managed by docker completely. They can be easily attached and removed from containers. You can backup your volumes also. This is the most used type of data storage.
Lets understand the docker volumes
Create docker Volume
Bellow command will create volume
docker volume create <volume_name>
docker volume create volume1
List all docker volumes with bellow docker command
docker volume ls
Inspect Docker Volume
Inspect the detail of Volume which you have created
docker volume inspect <volume_name>
docker volume inspect volume1
Remove Docker Volume
Remove docker volume which is created
docker volume inspect <volume_name>
docker volume inspect volume1
Remove All Docker Volumes at Once
Bellow command will remove all volumes which are created in your system. It will ask for confirmation, if everything looks good you can say yes.
docker volume prune
Attach Volume with Docker Container
There are two commands you can use to mount volume with container check bellow.
docker run -it -d --name <container_name> --mount source=<volume_name>,target=/<folder_name> <image_name>
docker run -it -d --name conA --mount source=volume1,target=/apps ubuntu
docker run -it -d --name <container_name> --volume <volume_name>,target=/<folder_name> <image_name>
docker run -it -d --name conB --volume flash,target=/apps ubuntu
You can use bellow command to check if you container was created or not
docker ps
You can use bellow command to inspect mount section of container
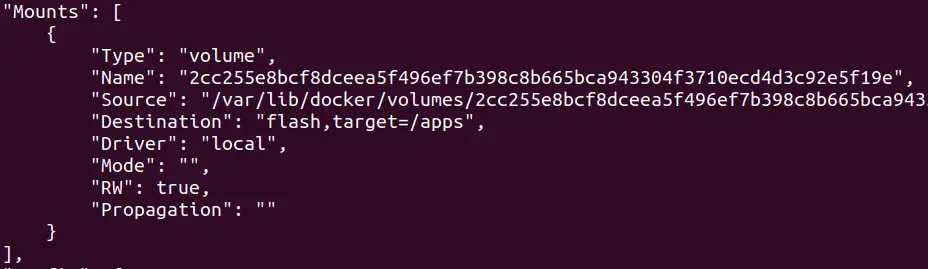
docker container inspect <container_name>
Readonly Docker Volume
We can attach readonly volume to docker container where docker container can read only files
docker run -it -d --name <container_name> --mount source=<volume_name>,target=/<folder_name>,readonly <image_name>
docker run -it -d --name conC --mount source=volume2,target=/apps,readonly ubuntu
Docker Bind Mount Storage
Bind Mount’s aren’t managed by docker and are mapped to host system directory.
Lets say we will mount the current folder in using pwd
docker run -it -d --name <container_name> --mount type=bind,source=<mount_directory>,target=/<working_dir> <image_name>
docker run -it -d --name conE --mount type=bind,source=$(pwd),target=/apps ubuntu
Let create an example, we will go inside container, create a file inside the folder by navigating to apps, then we can see that file in container and outside container
docker exec -it conE bash cd apps touch hello.txt ls exit
You can also create readonly bind mount using bellow command
docker run -it -d --name conF --mount type=bind,source=$(pwd)/docker_bind,target=/apps,readonly ubuntu
Docker TMPFS Mount Storage
This type of storage maps to the Host systems(Linux) memory Tmpfs is not persistent lice volumes and Imps and gel removed when the container they are attached to are stopped. They only ever get mapped to a a single container in file* lifetime. Allows you store more temporary data without affecting a container’s efficiency.
docker run -it -d --name <container_name> --mount type=tmpfs,target=/<working_directory> <image_name>
docker run -it -d --name tempCon --mount type=tmpfs,target=/apps ubuntu
Inspect the mount sections with bellow command
docker container inspect tempCon
Another way to create TMPFS mount
docker run -it -d --name <container_name> --tmpfs /apps <image_name>
docker run -it -d --name tempCon1 --tmpfs /apps ubuntu
Docker Storage Drivers
In situation where you have to write in the Dockers writable layer you can make use of specific storage drivers. These will allow you to maintain control over haw docker images 8 containers are managed and stored. Here are a few of the storage drivers.
Examples drive used for docker are Overlay2, awls, dovkomappor, btrfs, vk
Next Tutorial